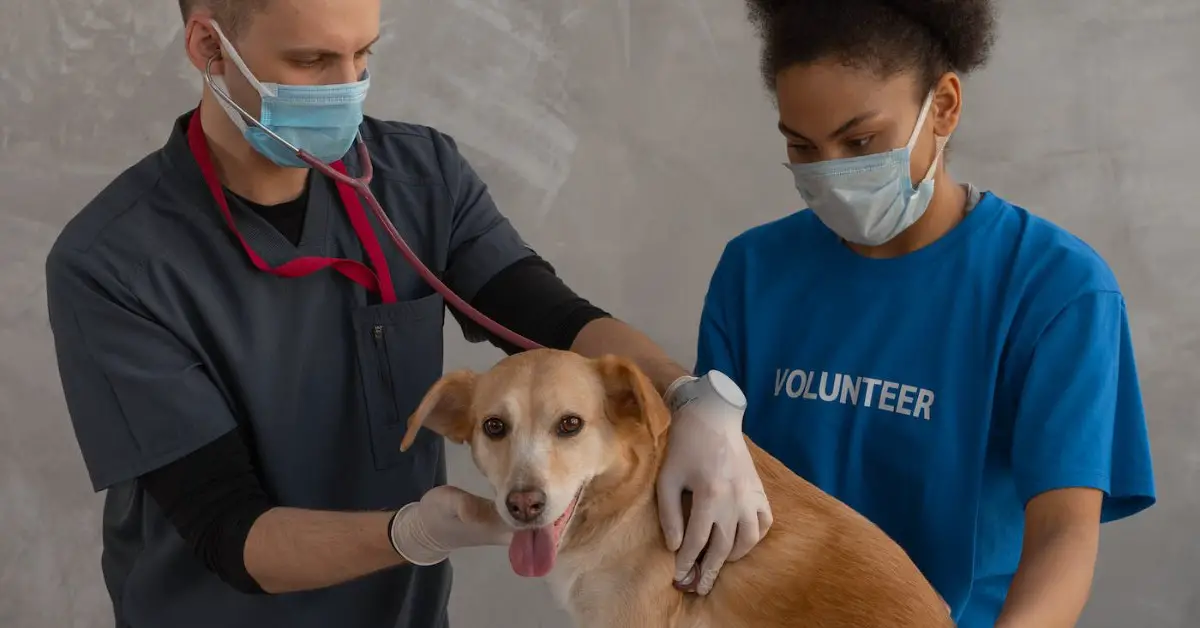
If you have a deep love for animals and a passion for their well-being, a career as a veterinarian may be a perfect fit for you.
Veterinarians play a crucial role in animal healthcare, providing medical care, diagnosing illnesses, and ensuring the overall health and welfare of animals.
In this comprehensive guide, we will outline the essential steps to becoming a veterinarian and provide valuable insights to help you succeed in this rewarding profession.
In our database, we also have an article that shows the steps to take to become a medical doctor if that interests you, take your time to read it.
Who is a Veterinarian?
A veterinarian is a trained medical professional who specializes in providing healthcare services to animals.
They are also known as veterinary surgeons or doctors of veterinary medicine (DVM), veterinarians are responsible for diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases, injuries, and other health conditions in a wide range of animals.
Are veterinarians in demand?
There is an increasing demand for veterinarians especially in Canada and the United States.
According to Job Bank Canada, the is a shortage of vets and over the period of 2022-2023 there will be new job openings with an expected total of 5,000 and about 4,300 new job seekers are expected to fill them.
In the United States, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there is an average of 4,800 openings for veterinarians each year. These openings, however, vary with states as some states experience greater demand than others.
Employment in this area is also predicted to grow by 19% from 2021 to 2031 much faster than other occupations.
So if this a new career path for you, it is really worth going into. Check out our category for different career options to see what might also suit you.
What are the steps to become a Veterinarian?
Step 1: Understand the Role of a Veterinarian
Just like every other career option, before getting started, you want to take your personal time and analyze, try to understand, and have a clear understanding of the role and responsibilities involved.
Veterinarians are highly skilled medical professionals who diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases in various animals. They provide medical care, perform surgeries, administer vaccinations, and offer guidance on nutrition and overall animal well-being.
The roles and responsibilities of a veterinarian include:
- Medical Care
- Preventive Medicine
- Surgical Procedures
- Diagnostic Procedures
- Emergency Care
- Client Education
- Research and Public Health
- Collaboration
Overall, veterinarians are dedicated professionals who work to promote and protect the health and welfare of animals.
Their roles extend beyond medical care to include advocacy, public health, and research, making them essential contributors to both animal and human well-being.
Step 2: Obtain a Relevant Education
After you have gotten a complete understanding of what it means to be a veterinarian, and if you have a passion for it, the next get a relevant related education.
You can do this by enrolling in some of the best veterinary schools near you and completing a bachelor’s degree or a diploma program.
To become a vet In Canada, you will have to complete at least 2 years of university studies followed by a 4-year doctorate of veterinary medicine before you advance for license exams.
So education is really important in your journey as a veterinarian. And while in school, select science-related courses that such as;
- Wildlife Biology
- Animal Science,
- Zoology or
- Pre-veterinary studies.
Additionally, to put the icing on the cake, consider pursuing specialized certifications or courses in veterinary medicine to enhance your knowledge and skills in the field.
Step 3: Gain Veterinary Experience
To strengthen your application and gain practical skills, it’s essential to acquire veterinary experience.
Therefore, during your undergraduate studies, aim to maintain a strong academic record and gain practical experience by volunteering at animal shelters, veterinary clinics, or research facilities.
This experience will expose you to different aspects of veterinary medicine and help you develop essential skills in animal handling, patient care, and diagnostics.
Step 4: Complete a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) Program
After obtaining a bachelor’s degree, you need to enroll in a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) program accredited by the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA).
The DVM program typically takes four years to complete and includes a combination of classroom instruction, laboratory work, and clinical rotations.
Step 5: Obtain Licensure and Certification
Following graduation from a DVM program, you must obtain a license to practice veterinary medicine in your desired jurisdiction.
The licensing requirements may vary by state or country but generally involve passing the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE).
Additionally, you may choose to pursue board certification in a specific area of veterinary medicine through specialized organizations such as the American Board of Veterinary Specialties (ABVS).
Step 6: Consider Specialization or Advanced Training
While not mandatory, specializing in a specific area of veterinary medicine can enhance your career prospects.
Specialties can include areas such as;
- Surgery
- Dermatology
- Cardiology, or
- Emergency medicine.
Advanced training programs, internships, and residencies are available for those who wish to pursue a specialization.
Step 7: Continue Learning and Professional Development
Veterinary medicine is an ever-evolving field, and it’s important to stay updated on the latest research, treatments, and advancements.
Participate in continuing education programs, attend conferences, and join professional organizations to expand your knowledge and skills.
Networking with other veterinarians can provide valuable insights and opportunities for collaboration.
Conclusion
Becoming a veterinarian requires dedication, compassion, and a genuine love for animals.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can lay a strong foundation for your career and embark on a journey that allows you to make a significant impact on animal health and welfare.
Remember to seek mentorship, gain practical experience, and continue your professional development to excel in this rewarding profession.
Please note that specific requirements and procedures may vary depending on your country or region.
It’s important to research and consult the veterinary licensing board or regulatory body in your area for accurate and up-to-date information on becoming a veterinarian.
Frequently Asked Questions
What qualifications do I need to become a veterinarian?
To become a veterinarian, you typically need to complete a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) program from an accredited institution.
This requires a bachelor’s degree, preferably in a science-related field, followed by four years of veterinary school.
How long does it take to become a veterinarian?
The path to becoming a veterinarian typically takes around eight years. This includes four years of undergraduate studies and four years in a veterinary school program.
Can I specialize in a particular area of veterinary medicine?
Yes, after completing your DVM, you have the option to pursue a specialization in areas such as surgery, dermatology, cardiology, or other specialized fields.
Specialization often involves additional training, internships, and residencies.
Do I need to be licensed to practice veterinary medicine?
Yes, you must obtain a license to practice veterinary medicine in the jurisdiction where you plan to work. Licensing requirements vary by country and state, but they generally involve passing a national licensing examination.
What skills are important for a veterinarian?
Veterinarians require a range of skills, including;
- Strong problem-solving abilities
- Good communication
- Interpersonal skills to work with pet owners
- Technical proficiency in diagnostic procedures and treatment methods, and
- Empathy for animals and their well-being.
Are there opportunities for veterinarians beyond the private practice?
Yes, veterinarians can work in various settings, including private practices, animal hospitals, research institutions, government agencies, zoos, and wildlife conservation organizations.
They can also pursue careers in academia and public health.
Related: